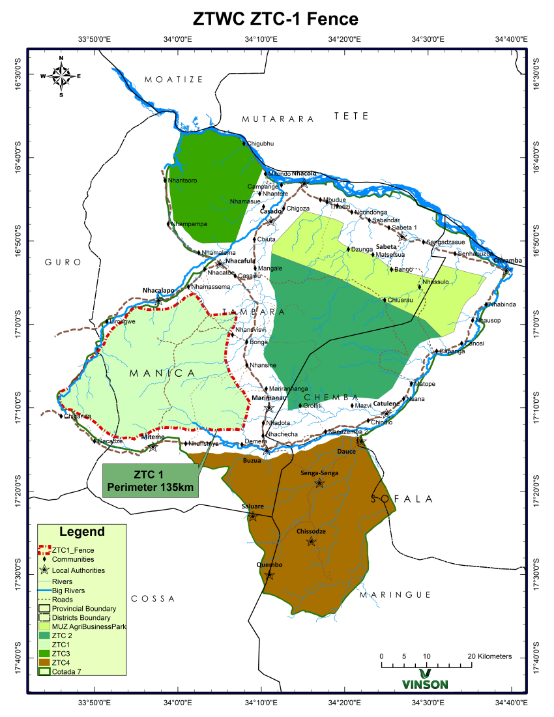
The main reserve is located in Manica province, and it straddles 90 % in Tambara and 10% Guru districts. The northern limit of the block borders with Nhacafula- Nyatsine CDA, the western limit borders with Nhacalapo CDA, eastern limit borders with Bonga- Marimanau CDA and the southern limit borders Chinganda-Muira- Miteme CDA. Magnitude wise, it is nearly 100 000 hectares, with a perimeter distance of about 160 kilometres. Elevation of the block fluctuates between 240 m to 540m above the sea level.
The eastern side of the ZTC1 is relatively flat with more of mopane/ combretum vegetation and sweet veld grass species. Western and southern parts are hilly and mountainous but very productive with several seasonal streams suitable for dam construction, and more terminalia/ sickle bush vegetation and mopane/ combretum vegetation. The whole ZTC1 niche is punctuated by the flamboyant baobab trees as flagship flora of Zambezi Tambara Conservancy. Overall, it is a sweet veld habitat suitable for all game species, but grass species are of high grazing value and sensitive to overstocking and overgrazing. More details will be available in the final veld assessments reports to be completed in May 2022. The research team has only identified grass species, ground coverage and composition percentages, as well as their grazing values. Fuel loads can only be obtained later in May when the grass is dry with seeds still intact.
This block will be mainly for, among other facets, ecotourism, conservation of general fauna and flora species. This concerns common wildlife species of Mozambique and those that adapt well in the low veld region. In the ZTC1 niche, all antelopes, lions and elephants are included and natural selection will govern the propagation of species. Elephants as a hyper browser will be governing the flora population ensuring a balance between grassland and woodlands. It is evident that high elephant numbers are needed to open mopane and sickle bush thickets, to promote more grass lands. The population could later be culled or translocated based on how the vegetation responds. The sustainable carrying capacity for ZTC1 is 5000 animals. New genetics can be exchanged among the blocks once in 10 years, and can also be replenished from other natural wildlife reserves within Southern Africa. On water provision, 25 boreholes coupled with waterholes are going to be drilled, meaning one borehole per every 4500 hectares. Furtherly, two earth dams shall be sited and constructed on streams with clean drainage, or less siltation.
Lodge Sites Identification Criteria
The lodge sites identification criteria is mainly based on accessibility from the existing backbone roads, underground water supply, camouflage, vantage view and topographical background landforms like hills, rock boulders and plains, with some sites surrounded by baobab trees. These factors create bush ambience for each lodge site, and each site has its own unique surroundings. Each lodge site will have its own water hole in front of the lodge, replenished by a solar powered borehole. In total 20 luxury lodges will be sited and constructed in this habitat. The lodge sites shall be more on the periphery of the reserve for accessibility and creation of less developed wild nucleus. An Environmental Impact Assessment will be conducted on each lodge site to achieve our Touching the Earth Lightly Policy.
There are small communities at Nhacalapo- Muira and Chiganda- Muira. Resettlement details presented in the following section “Community Development Plan”. .